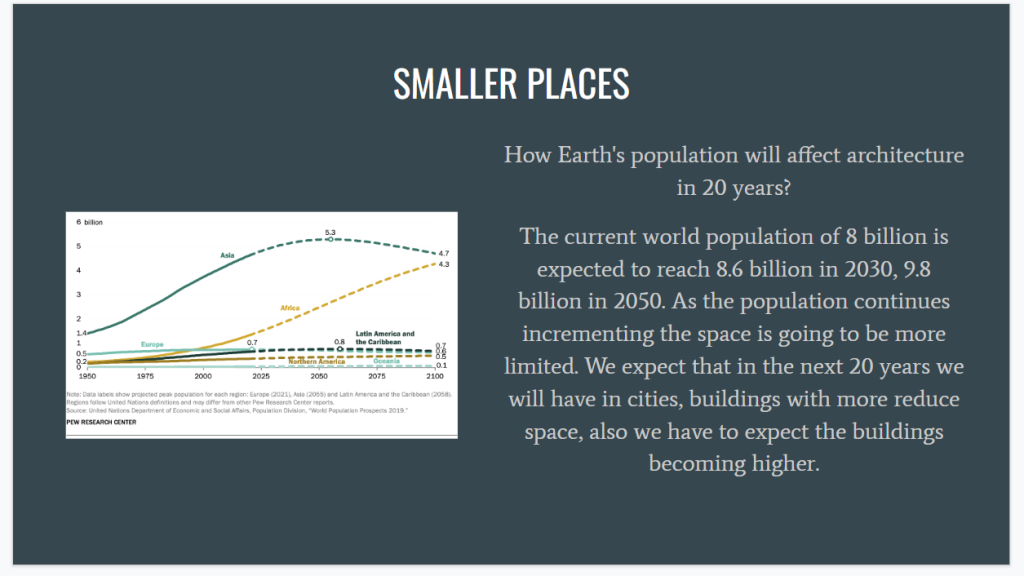
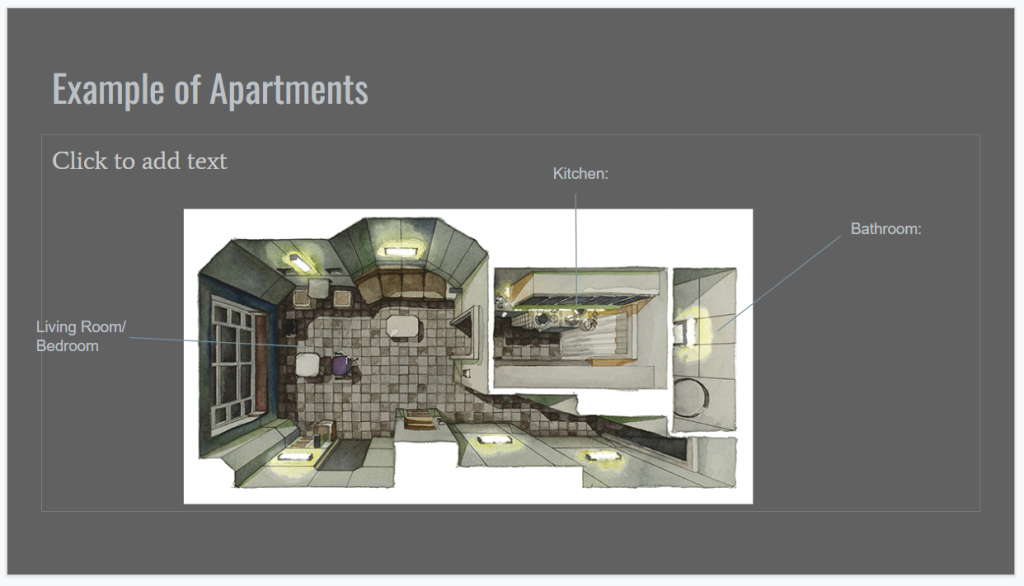
The origins
We start with the first hominids that appeared in central Africa. They lived in the equatorial zone, in a warm climate. Their major physical features were upright posture and bipedal locomotion. They moved northwards, obtaining new characteristics: the stilt walking and chewing wildlife to obtain food.
Palaeolithic period
Herectus (about 1.9 million years ago) lived at many places in Africa and Europe. The date of his appearance is not known, but it is thought that he was present in Asia by 2 million years ago. He probably arrived in Spain about 850,000 years before the present day, because the first fossil human skulls have been excavated there.
The terra amanta appeared, a new discovery of 12 Homo erectus huts, along with a dune landscape and plant remains, indicates that this group of people lived in what is now Morocco from between 1.85 million BC to 1.75 million BC. The find raises exciting questions about when and how humankind first began to build permanent shelters as well as our understanding of how Homo erectus lived and worked together.
The Palaeolithic is the period between 100,000 BCE and present. In Europe, Homo erectus is discovered in early this period. He inhabits cave networks in North Africa and the East. By 40,000 BCE, we have the emergence of neanderthalensis that lives in separated groups. They live in common caves in Iraq and they also practice large-scale burial of their dead. The monumental stone statues that were discovered indicate a belief in the continuity of life after death which indicates primitive but advanced mentality.
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is the region in the vicinity of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, where writing is developed and domestic pottery is developed. The architecture is made with adobe or brick. The most characteristic buildings of ancient Mesopotamia are the Ziggurats (stepped and pyramidal towers), which appear circa 3,000 BCE.
Egypt
In order to understand the Egyptian people and architecture it is necessary to consider the Nile River. Egypt develops a civilization that survives almost 3,000 years. temples, cities and fields follows these two perpendicular axes forming an orthogonal grid. Lahum, city founded by Sesostris II since 1,895 BCE. City of LahumTemples The temple is the most important public building, place of veneration and center of learning and training for the administration of the country. It represents the architecture of permanence and immutability. Its shape experienced few subtle changes in 2,700 years with the same shapes and details. Large masses and monotonous regularity expressed solidity as a symbol of durability, guarantee of safety and unbreakability. . Pyramids, Egyptian were obsessed with life, too good to end, hence the cult of dead reflected in the pyramids, eternal constructions.
Ancient Greece
The Greek architects experimented with a variety of materials and used them to achieve aesthetically pleasing and practical works of art. The Greeks used architectonic proportions to form the grids of their buildings, and they used every possible inch of space to create beautiful structures. The Greek civilization was one of the most important in the history of mankind, it was a civilization that developed during the 6th and 5th centuries BC. This civilization has been called «one of the most advanced ever seen.» The Greeks were greatly influenced by many cultures which made their culture unique. Their art and architecture incorporated multiple influences from those cultures.
Roman legacy
Ancient Rome was a complex social, economic, and military system. It was highly influenced by the culture of Greece and Egypt. In art, architecture, and religion after the fall of the Roman Empire which declined and became Christianized. Churches and other religious buildings were the only important architecture, while public and private buildings were submerged in relative anonymity. The glory of pagan imperial Rome was lost, as a new Christian empire was established in the East, with religious and civil powers merged together. With this came a decline in pictorial, sculptural and constructive techniques as well as everything that was not related or justifiable with the new religion such as classical language from the cultures of Greece and Rome vanished between 5th-15th centuries in Middle Ages but then continued on later stages from Renaissance (15th century) to Modern Age
Renaissance
Modern architecture came of age in Florence. The use of the classical forms and the revival of ancient Roman works were renewed here. Stucco, copper and marble were used in their original form, but also new materials were introduced, such as concrete, glass and iron (especially with Brunelleschi). A great number of churches, churches, palaces and private houses have been built in this period. The style is rational, severe and severe proportions. It is magnificent aesthetics based on rigorous mathematics, geometric perspective drawing and ideal proportions applied to sculpture. Optimism and confidence in human potential arise. Humanism was a philosophy that emphasized the importance of human values and achievements, distinguishing them from religious dogma. Vitruvius man, by Leonardo da Vinci. Plato’s ideal figures were recovered: circle, square and equilateral triangle. Hence symmetry and proportion were basic to the project and the system of ideal proportions laid on the human body.
Neoclasical styles (theorical neoclasicism):
was the linked to the idea of public services and educational functions of the buildings as well as the greek agora.
Étienne-Louis Boullée and Claude-Nicolas Ledoux were the representatives of this new «talking architecture» they have visionary designs, with pure geometric forms this kind of ideas were coming up to an Utopian Neoclassicism.
The 19th Century
the enlightment make the realization of the industrial revolution an the migrations form town fiels to the cities were huge. population and a migratory phenomenon towards the cities, which
were left insufficient space. The expansion began with industrial and worker neighbourhoods, new construction typologies appeared. for example:
industrial units or naves, stations, hangars, markets, sanitary infrastructures, pavilions.
Also new materials appeared: cast, iron and glass.
This expantion also bring the polythecnic schools and new international exhibitiones were presented and brings up the experimentatrion of new materials and shapes.
the alienation of new experimental spirit was made to those who think that way. Many would prefer to stay in the shadow, ignore it, and most have a desire form the past so that will be the begining of the historicism, exoticism, and a mixture of various elements.
Antimachinism
Anti-Machinism was a critical current linked to Romantic picturesqueness that rejected the dreariness of the real world and longed for a return to an idealised medieval world based on the work of guilds.
the most representatives of the movementes were: John Ruskin and William Morris.
Morris designed the interior of the Red House and promoted the Arts-and-Crafts movement.
20th Century
Art Nouveau, Modernism, Liberty, Jugendstyl
It is characterized by clean lines, curves and undulating inspired by nature (Organicism) and oriental art, with geometric formal simplification towards two-dimensionality (Geometric trend). Japanism and romantic symbolism; as well as the handcrafted production promoted by Ruskin and Morris do with medievalism.
the most important artist of this is Antoni Gaudí went through a modernist period, but later he produced an original architecture, typical of Catalonia, based on the Mudejar tradition and the medieval past. He used the trencadís technique, a kind of mosaic made from fragments of ceramic tiles joined with mortar.
Architecture of the future